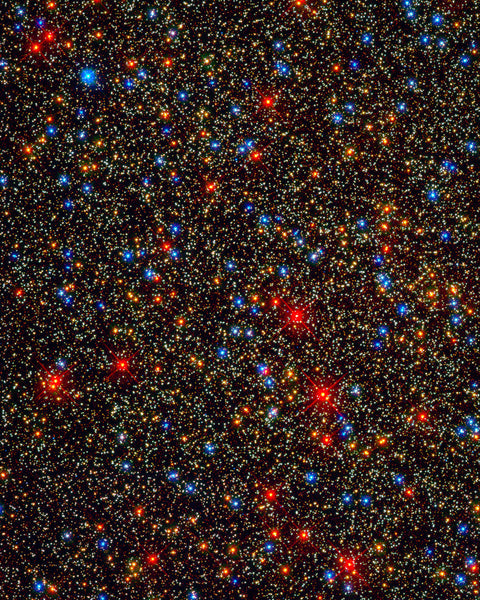
Stars Galore Globular Star Cluster Omega Centauri
NASA's Hubble Space Telescope snapped this panoramic view of a colorful assortment of 100,000 stars residing in the crowded core of a giant star cluster.
The image reveals a small region inside the massive globular cluster Omega Centauri, which boasts nearly 10 million stars. Globular clusters, ancient swarms of stars united by gravity, are the homesteaders of our Milky Way galaxy. The stars in Omega Centauri are between 10 billion and 12 billion years old. The cluster lies about 16,000 light-years from Earth.
This is one of the first images taken by the new Wide Field Camera 3 (WFC3), installed aboard Hubble in May 2009, during Servicing Mission 4. The camera can snap sharp images over a broad range of wavelengths.
The photograph showcases the camera's color versatility by revealing a variety of stars in key stages of their life cycles.
The majority of the stars in the image are yellow-white, like our Sun. These are adult stars that are shining by hydrogen fusion. Toward the end of their normal lives, the stars become cooler and larger. These late-life stars are the orange dots in the image.
Even later in their life cycles, the stars continue to cool down and expand in size, becoming red giants. These bright red stars swell to many times larger than our Sun's size and begin to shed their gaseous envelopes.
After ejecting most of their mass and exhausting much of their hydrogen fuel, the stars appear brilliant blue. Only a thin layer of material covers their super-hot cores. These stars are desperately trying to extend their lives by fusing helium in their cores. At this stage, they emit much of their light at ultraviolet wavelengths.
When the helium runs out, the stars reach the end of their lives. Only their burned-out cores remain, and they are called white dwarfs (the faint blue dots in the image). White dwarfs are no longer generating energy through nuclear fusion and have gravitationally contracted to the size of Earth. They will continue to cool and grow dimmer for many billions of years until they become dark cinders.
Other stars that appear in the image are so-called "blue stragglers." They are older stars that acquire a new lease on life when they collide and merge with other stars. The encounters boost the stars' energy-production rate, making them appear bluer.
All of the stars in the image are cozy neighbors. The average distance between any two stars in the cluster's crowded core is only about a third of a light-year, roughly 13 times closer than our Sun's nearest stellar neighbor, Alpha Centauri. Although the stars are close together, WFC3's sharpness can resolve each of them as individual stars. If anyone lived in this globular cluster, they would behold a star-saturated sky that is roughly 100 times brighter than Earth's sky.
Globular clusters were thought to be assemblages of stars that share the same birth date. Evidence suggests, however, that Omega Centauri has at least two populations of stars with different ages. Some astronomers think that the cluster may be the remnant of a small galaxy that was gravitationally disrupted long ago by the Milky Way, losing stars and gas.
Omega Centauri is among the biggest and most massive of some 200 globular clusters orbiting the Milky Way. It is one of the few globular clusters that can be seen with the unaided eye. Named by Johann Bayer in 1603 as the 24th brightest object in the constellation Centaurus, it resembles a small cloud in the southern sky and might easily be mistaken for a comet.
Hubble observed Omega Centauri on July 15, 2009, in ultraviolet and visible light. These Hubble observations of Omega Centauri are part of the Hubble Servicing Mission 4 Early Release Observations.
Great care has been taken to reproduce this image for you. We stand behind the quality of your print with a 100% customer satisfaction guarantee.